IJCNC 02
SIMULATED ANNEALING-SALP SWARM ALGORITHM BASED VARIATIONAL AUTOENCODER FOR PEAKTO-AVERAGE POWER RATIO REDUCTION
Prabhakar Narasappa Kota1, Pravin Balaso Chopade 1, Bhagvat D Jadhav 3, Shriram Sadashiv Kulkarni 4 and Pravin Marotrao Ghate 3
1 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, M. E. S. Wadia College of
Engineering, Pune, India
3Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, JSPM’s Rajarshi Shahu College of
Engineering, Tathawade, India
4Department of Information Technology, Sinhgad Academy of Engineering, Kondhwa,
Pune, India
ABSTRACT
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) have achieved significant advancements in spectral effectiveness and data rates within wireless communication systems. However, it is accompanied by a critical challenge: the high Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR). This issue demands attention and effective solutions to ensure optimum performance and reliability of OFDM-based systems. Currently, deep Learning (DL) algorithms perform well on end-to-end wireless communication systems. This study introduces a novel approach to PAPR reduction in OFDM systems by integrating a Simulated Annealing- Salp Swarm Algorithm (SA-SSA) with a Variational AutoEncoder (VAE). The proposed method effectively mitigates peaks while preserving favorable spectral properties, thereby facilitating seamless PAPR migration. The SA-SSA – based VAE method is used to develop a peak-canceling signal method depending on the input signal which reduces the PAPR signal. Constellation mapping and remapping of symbols are considered in each subcarrier of the VAE method that minimizes the Bit Error Rate (BER) and PAPR in OFDM systems. To further improve the performance of VAE, proposed an SA-SSA algorithm that tuned the hyperparameters of the VAE method to select optimum hyper parameters of VAE for better performance. The performance of the developed method is analyzed with characteristics of BER, Symbol Error Rate (SER), and Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF) under various subcarriers. The proposed method obtained less PAPR of 1.9 dB, 2.0 dB, 2.4 dB, 2.8 dB, and 3.2 dB for 64, 128, 256, 512, and 1024 subcarriers which is less when compared to existing methods like Hyperparameter Tuned Deep Learning based Stacked Sparse Autoencoder (HPT-SSAE and Conditionally Applied Neural Network (C- ANN).
KEYWORDS
Deep Learning, Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing, Peak-to-Average Power Ratio, Simulated Annealing-Salp Swarm Algorithm, Variational AutoEncoder
1. Introduction
The recently implemented Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation method in mobile systems breaks down the fast time-varying channel [1-4]. However, multicarrier modulation techniques like OFDM modulation is challenged with high PAPR problems, which result in inter carrier interference due to the non-linear terms of high-power amplifier(HPA) [5-9].Generally, HPA is required to process in the linear are a which results in high adjacent channel interference and degrades the performance of the Bit Error Rate (BER) [10]. The above situation provides ineffective amplification and maximizes the cost of hardware. To address these problems, several PAPR reduction algorithms have been developed in previous studies [11], [12]. Particularly, the clipping method restricts the PAPR below the threshold value which causes differences in degrees of signal distortion [13]. In recent times, Deep Learning(DL) algorithms have gained attention in the field of image classification and detection of objects. By their powerful ability of feature extraction, Deep Neural Network (DNN) has been implemented in communication systems like estimation of channels and detection of signals [14]. The existing researchers implemented DL algorithms for solving the issue of high PAPR in OFDM systems and attained enhancement in conventional methods [15]. The AutoEncoder (AE) is one of the majorly utilized DNN structures that showed high potential in minimizing PAPR [16]. The AE is a feed-forward neural network consisting of anencoder and decoder, in whichthe encoder converted input signal to less dimensional representation and decoder reconstructs input signal from representation [17], [18]. Next, the whole communication system depending upon AE can be optimized in an end-to-end manner by reducing loss function with theknowledge of the transmitter and receiver [19]. This research used the VAE method for PAPR reductioninOFDM modulation. This research employs the VAE technique, wherethe encoder is trained to minimize PAPR while the decoder reconstructs the original signal at the receiver. To further improvetheperformance of the VAE method, hyperparameter tuning is performed by the SA-SSA algorithm for balancing the PAPR reduction and performance of BER. Then, thetraining process is implemented to improve the convergence of developed method. The primary objective of the manuscript is to develop the effective method for PAPR reduction in OFDM system through integrating the SA-SSA with VAE technique. It minimizes the PAPR when preserving the spectral properties and enhancing the SER and BER performance. Then, optimize the hyperparameters of VAE by utilizing SA-SSA algorithm for balancing the exploration and exploitation abilities, ensures the optimum performance under different conditions and subcarriers. The essential contributions of the research are given as:
- This research proposed a Simulated Annealing-Salp Swarm Algorithm (SA-SSA) based Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) for the PAPR reduction method in OFDM system which trains a network based on label data for reducing PAPR with less minimization of BER.
- To improve the VAE performance, the hyperparameters are tuned by the Simulated Annealing-Salp Swarm Algorithm (SA-SSA) which selects optimum hyperparameters of VAE that lead to better performance.
- The proposed algorithm is simulated with MATLAB and analyzed with Bit Error Rate(BER), Symbol Error Rate (SER), and Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF) under different subcarriers to compare performance with existing algorithms.
This research manuscript is given as follows: Section 2 illustrates a literature review of recent research. Section 3 explains the details of proposed methodology and Section 4 gives results, a comparative analysis, and a discussion of the developed method. The conclusion of this manuscript is given in Section 5.
2. Literature Review
Jayamathi. A and Jayasankar. T [20] implemented a Hyperparameter Tuned Deep Learning based Stacked Sparse Autoencoder (HPT-SSAE) method for PAPR minimization. The implemented method was used for creating a peak-canceling signal depending on features in the input signal. Constellation mapping and symbols demapping were considered on every subcarrier by SSAE method which reduced BER and PAPR of OFDM. For enhancing SSAE performance, the hyperparameter tuning was performed by the Monarch Butterfly Optimization (MBO) algorithm.
The implemented method has less PAPR execution, however, still there is high energy consumption while data broadcasting.
Srinivas Ramanathan et al. [21] introduced a Hybrid Partial Transmit Sequence (PTS) Companding algorithm for PAPR reduction. The introduced method used the PTS technique and companding for developing hybrid PAPR reduction. In the introduced method various segments of data block signal and overlapping factor were utilized to determine the number of data segments in every segment. To obtain less signal energy in every segment, select a good data block for transmitting and analyzing further overlapping data blocks. Next, the signal peaks were compressed by companding. The introduced method minimized the PAPR however, the method required a high number of repetitions to obtain the desired outcome which provided a high execution time.
Hamada Esmaiel et al. [22] presented a Time-Domain Synchronous Index Modulation(TDS-IM) OFDM named as DL-based TDS-IM-OFDM-SS for PAPR reduction. In the presented method, the DL receiver eliminated the environmental dependency and simplified the complexity of the system. The method established identification parameters, attaining correct estimation of modulation symbols in complex channels. The outcomes of the simulation showed the effective performance of the presented method in spectral and energy effectiveness and also their ability to minimize the method’s BER. However, the presented method failed to change velocity size to carry out the optimum point exploration.
Eldaw E. Eldukhri et al. [23] developed the Conditionally Applied Neural Network (C-ANN) method for PAPR reduction. Developed method compressed peaks of destinated subcarriers by slightly shifting the positions of respective frequency samples without impacting their phase orientations. To cover a wide range of applications, peak threshold of subcarrier was selected for the saturation phase of the nonlinear energy amplifier. Optimum values of factor-controlled the peak threshold were acquired which reduced PAPR and BER levels. The developed method does not need a recovery procedure at the receiver which makes less computation complex. However, the developed method was not suitable for the huge number of sub-carriers.
Ezmin Abdullah et al. [24]suggested an Asymmetrical Autoencoder (AAE) method for reducing high PAPR in CP-OFDM devices. The suggested method used 4 AAE methods and their performance was analyzed depending on comprehensive parameters like training in various phases, length of cyclic prefix, up sampling parameters, and loss function phases. The examination of AAE in5G CP-OFDM devices has a high performance by the AAE method which minimized the substantial quantity of PAPR, BER minimizes, and execution complexity. However, the PAPR diminished but couldn’t moderate the non-linearity.
Sivaprasad Valluri et al. [25] implemented an effective PAPR reduction method that maintained PAPR without maximizing mean energy. In the implemented method, the optimum orthogonal precoding matrix depended on Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) was created to minimize the mean power of the system. Due to this optimum precoding matrix that can’t effectively minimize PAPR, then introduced a method known as peak samples which reduced peak and mean energy. However, the count of sub-carriers at the transmitting end was comparatively high and that maximized the execution complexity.
Abhiranjan Singh and Seemanti Saha [26] presented a Machine Learning (ML) that depended on estimation and signal detection for OFDM. In the presented method, ML techniques were trained by known pilot sequences in high SNR scenes taking channel imperfections happening together. After the method was trained, it was utilized for estimating and detecting signals corrupted through different channel imperfections at the receiver. The presented method obtained less BER rate and PAPR with less computational cost. However, the method was not suitable for a huge count of sub-carriers.
3. Proposed Methodology
The signal transmission using a transceiver-based OFDM system is a generally employed method for PAPR reduction. That separates the efficient spectrum channel into a group of orthogonal subchannels with the same bandwidth, every sub-channel controls separate information by individual subcarrier. Additionally, OFDM signals are every individual subcarrier. With multiple carrier systems of signal transmission, input information of binary sequences is mapped to a group of symbols by modulation method. Then, 𝑁 symbols 𝑋 = [𝑋0,𝑋1,𝑋𝑁−1]𝑇are assigned to the IFFT component to modulate of each subcarrier and obtain OFDM signal in the time domain 𝑥= [𝑥0,𝑥1,…,𝑥𝑁−1]𝑇. The mathematical formula for covering of OFDM signal on discrete-time domain is given in Eq. (1),
Where𝑁 represents the number of subcarriers and 𝑋𝑘represents 𝑛𝑡ℎ complex symbol processed and sent by 𝑘𝑡ℎ sub carrier. In the above eq (1), signal in time domain is generated through IFFT including 𝑁 modulated and orthogonal subcarriers with highest PAPR whether updating it to result of IDFT block. The mathematical formula of PAPR of OFDM signal from discrete-time is given in Eq. (2),
The high PAPR from OFDM signals resulted in signal distortion that caused minimization of BER performance. It is essential to minimize the PAPR of OFDM signals, which maximizes the effectiveness of the power amplifier and maintains the performance of BER.
3.1. Variational Auto Encoder (VAE)
In this research, the PAPR is minimized using SA-SSA based VAE technique. The VAE learns the encoder process from the input OFDM signal for representation of less PAPR and the decoder process from less PAPR representation to input space, so the reconstruction resulted in less BER loss. AutoEncoder (AE) is one of the frequently used Deep Neural Network (DNN) architectures and showed high potential in minimizing PAPR. AE is a feed-forward neural network including an encoder and decoder, in that encoder converted input signal to a less dimensional representation when the decoder reconstructed the input signal from this representation. Next, the whole communication system depending upon AE is optimized by reducing loss function without the knowledge of the transmitter and receiver. So, variational autoencoders used in this research can handle non-linear and linear transformations and a VAE method minimized the dimension of difficult datasets through neural network algorithms. The VAE adopted backpropagation to learn features at a certain period on method training and developing phases, which is much more prone to obtaining data overfitting. Figure 1 represents basic architecture of a variational autoencoder.
Figure 1. Basic structure of variational autoencoder
Here, 𝑋 represented as a group of whole samples in actual data, where 𝑥𝑖describes 𝑖𝑡ℎ sample. The encoder is process 𝑔(𝑋) which encodes actual data to 𝑧,which is 𝑧 = 𝑔(𝑋), where the dimension of 𝑧 is essentially less than 𝑋. After that, the simplified data is fed to the decoder that decodes𝑧 and outputs 𝑋̃. Therefore, the decoder is represented as 𝑋̃=𝑓(𝑧).The loss function 𝑙= ‖𝑋 −𝑋̃‖2is utilized for estimating the closest among 𝑋 and𝑋̃. If the magnitude of 𝑙 is small, the method is considered as efficient. Assume that encoded 𝑧 included as much valuable data from𝑋, which struggled to describe actual data after the reduction of dimensionality during the process of method training. Let 𝑋∈ 𝑅𝑐×𝐻×𝑊is the image, here 𝐶,𝐻𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑊 are dimensions which store data of𝑋. The whole aim is to train an autoencoder that encodes images to 𝑧 ∈ 𝑅𝑑(which is dimensionality reduction),next decoder which reformulated an image as 𝑋̃∈ 𝑅𝐶×𝐻×𝑊therefore lossfunctionisreduced.Practically,themethodcandevelopusefulattributesoftheimageas well as unnecessary noise elements due to 𝑧 distribution which is represented as 𝑝(𝑧).For that drawback, Variational AutoEncoder(VAE)is used for probabilistic distribution of 𝑧,before whole necessary 𝑋attributes are extracted to create 𝑧 sampling space and passed to the decoder. Assume,𝑧 ∽ 𝑁(0,𝐼),where𝐼describes the identity matrix, that represents 𝑧 is regarded as multiple dimensional random variables which obeyed classical multiple variate Gaussian distribution. Represent 𝑋 and 𝑧 as random variables and 𝑖𝑡ℎ respectives ample are represented as 𝑧𝑖and𝑥𝑖. The result is produced by a stochastic procedure of two stages, with 𝑧 considered as a hidden variable. Initially, the prior distribution of 𝑋 is encoded and sampled for obtaining𝑧𝑖and then depended on conditional distribution 𝑝(𝑧𝑖), data point 𝑥𝑖is obtained. For the decoding procedure, samples 𝑧𝑖acquired from 𝑁(0,𝐼) distribution are implemented to the decoder, next parametrized decoder establishes mapping which results from a 𝑧𝑖precise distribution respected to 𝑋 that is represented as 𝑝𝜃(𝑧𝑖). For simplifying the difficulty of statistics, consider that 𝑋 obeyed isotropic multivariate Gaussian distribution represented as 𝑧𝑖. That represents after 𝑧𝑖 is implemented to decoder, distribution of 𝑋|𝑧𝑖 is acquired after fitting 𝜇′and𝜎′2. The mathematical formula is given as Eq.(3),
Next, Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) is assigned for estimating 𝜃 depending on attained X. Mathematical formula is given in Eq. (5),
Where, 𝑊𝑓 and 𝑏𝑓 represents weight and bi as of 𝑙𝑓−𝑡ℎ encoding unit. Then, encoded symbols 𝑙𝑓 𝑙𝑓 Are passed through IFFT process which generates transmitting signals. After that, signal is passed through wireless channel to arrive at receiver. Finally, received signal passed through the FFT process and processed decoding through VAE. That is taken as a decoding unit which has sub- blocks similar to an encoding unit. Hence, the mathematical formula for the output of the decoding unit is given as Eq. (7),
Where 𝑦 represents input for decoding and 𝑊𝑔 and 𝑏𝑔 represents weight and bias of 𝐼𝑔−𝐿𝑔 𝐼𝑔 𝑡ℎ decoding. A mathematical formula for recreated symbol at receiver end is given in Eq. (8),
𝑟 = 𝑔 ∘ 𝐹𝐹𝑇 ∘ 𝐻 ∘ 𝐼𝐹𝐹𝑇 ∘ 𝑓(𝑟) (8)
Where 𝐻 represents effect of wireless channel.
3.2. Hyperparameter Tuning by SA-SSA Optimization Algorithm
The parameters of VAE used for hyperparameter tuning are weight matrix, bias, and activation function. The optimization algorithm selects a set of optimum hyperparameter values for the VAE method, that value is utilized to control the learning process and improve the performance of the VAE method. So, the SSA used in this research is the meta-heuristic algorithm that has iteration, leaders lead followers and move towards food in chain behavior. This research proposed a Simulated Annealing-Salp Swarm Algorithm (SA-SSA) which extended an application of space algorithm to enhance the optimization capability of SSA. The space algorithm is referred as Symmetric Perturbation-based SA mechanism in SA-SSA technique which enhances the optimization ability of traditional SSA. Initially, logistic mapping is utilized for population initialization to improve diversity of population. Next, symmetric adaptive division of population is implemented for balancing development and exploration capacity of SSA. At last, SA depends on symmetric perturbation which is implemented in SSA to enhance the performance of traditional SSA algorithms.
3.2.1. Initialization
Initially, the SSA performed population initialization. 𝑁 represents Salp’s population size and 𝐷 represents a dimension of spatial, 𝐹 = [𝐹1,𝐹2,…,𝐹𝐷]𝑇represents food present in space. The lower and upper bounds of search space are represented as 𝑙𝑏 = [𝑙𝑏1,𝑙𝑏2,…,𝑙𝑏𝐷]and 𝑢𝑏 = [𝑢𝑏1,𝑢𝑏2,…,𝑢𝑏𝐷]. Next, the initialized location of 𝑥𝑖 salp in random number, 𝑖=1,2,…,𝑁,𝑗=1,2,…,𝐷. The mathematical formula for the initial position is given in Eq.(9),
Next is to update the leader’s position. A leader is responsible to identifying food and guiding activities of whole team. The mathematical formula for position update of leader is given in Eq. (10),
In the above eq (10), 𝑥𝑗 1 describes the position of leader, 𝐹𝑗 represents the position of food, 𝑢𝑏𝑗 and 𝑙𝑏𝑗 represents upper and lower bound. 𝑐1, 𝑐2𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑐3 are control parameters between that 𝑐2𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑐3 represents random numbers with range [0,1], 𝑐2 manages the size of steps and 𝑐3 manages direction. 𝑐1 represents an essential control parameter that balances exploration and growth ability of SSA on iteration. To make algorithm process the global search in an initial iteration and correct development in next part, mathematical formula for 𝑐1 is given as Eq. (11),
𝑐1=2𝑒−(4𝑙/𝑀𝑎𝑥_𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛)
Where 𝑙 represents the present iteration and 𝑀𝑎𝑥_𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 represents the highest iteration. Finally, update location of follower. The location of the follower is related to their first location, speed of motion, and acceleration. The pattern of motion conformed to Newton’s law of motion. The mathematical formula for 𝑅moving distance of follower is given in Eq. (12),
Where, 𝑡 represents the time which is variation value of iteration, so 𝑡 = 1,𝑣0 represents a follower’s first speed that is 0, 𝑎 represents the follower’s acceleration and the mathematical formula for calculating 𝑎 is given in Eq. (13),
𝑎=(𝑣𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙−𝑣0)⁄𝑡 (13)
The follower followed the moving of the preceding salp near to themselves, mathematical formula for moving speed is given in Eq. (14),
Where, 𝑡=1 and 𝑣0=0, hence mathematical formula for calculating R is given in Eq.(15),
The mathematical formula for update of follower position is given in Eq.(16),
Where, 𝑥𝑗𝑖′ represents a location of 𝑖𝑡ℎ follower in 𝑗𝑡ℎ dimension space before updation and 𝑥𝑗 𝑖 represents the location of the follower after updation
3.2.2. Simulated Annealing-Salp Swarm Algorithm (SA-SSA)
This research developed a SA-SSA which extended the application of the space algorithm to enhance the optimization capability of SSA. Initially, logistic mapping is utilized for population initialization to improve the diversity of population. Next, symmetric adaptive division of the population is implemented for balancing development and exploration capacity of SSA. At last, SA depended on symmetric perturbation is implemented to SSA to enhance performance of traditional SSA algorithm. Figure 2 describes process of SA-SSA algorithm.
Figure 1. Process of SA-SSA algorithm
3.2.3. Logistic Mapping-based Population Initialization
The swarm intelligence algorithm is a process of population iteration, so population initialization has a straight effect on the last solution and also impacts the capacity of optimization. The much more abundant population initialization is much more feasible to identify the solution of the global optimum of population. Without the support of knowledge, many algorithms randomly initialize the population that highly impacts an algorithm’s performance. The chaotic sequence contains random characteristics and a population initialization is a chaotic sequence that has good diversity. The chaotic sequences generally utilized at current iterative, tent, logistic mapping, etc., Mathematical formula for logistic mapping is given in Eq. (17),
Where, 𝑝 represents an adjustable parameter, generally set to 4. Population size is represented as 𝑖 = 1,2, … , 𝑁 and 𝑗 = 1,2, … ,𝐷 is a count of chaotic variables. The mathematical formula for population after logistic mapping is given in Eq. (18),
3.2.4. Symmetric Adaptive Population Division
In traditional SSA, count of leaders and followers is half of Salp’s population, which leads to search asymmetry. In initial iteration, count of leaders is less and proportion is less that causes ineffective global search and falls to local optimum. Though, in later iteration, count of followers is less which causes ineffective local search and less optimization accuracy. To overcome these limitations, this research introduced a symmetric adaptive division population that adjusted the count of salp leaders which represents the adaptive minimizing trend as number of iterations, when number of followers represents adaptive maximizing trend. That made SSA algorithm concentrate much on global exploration in initial phase and close to an optimum value in the next phase, which improved optimization accuracy. The mathematical formula for symmetric adaptive population division with 𝜔 control parameter is given in Eq. (19),
Where 𝑙 represents the present iteration number and 𝑀𝑎𝑥_𝐼𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 describes the highest iteration number and 𝑏 represents the ratio coefficient that is utilized for avoiding proportion imbalance. 𝑘 Represents the disorder deviation factor and minimizing 𝜔 value distributed in integration with the rand function.
3.2.5. Symmetric Perturbation-based Simulated Annealing Mechanism
The SA algorithm produces a new solution depending on a present solution in certain way and accepts a new solution with some probability, which improves local jumping capability of algorithm and keeps algorithm in high diversity for the next iterations. New solutions generation is specifically significant in SA. This research introduced symmetric perturbation for producing new solutions based on the SA algorithm. Symmetric perturbation is defined as the mapping of a location to present an optimum location in a symmetrical interval. It is defined through the product of present temperature and random number located for dimension space. The mathematical formula for symmetric perturbation is given in Eq. (20),
By the metropolis criterion, the mathematical formula for sampling is given in Eq. (21),
Whether, 𝑑𝑓 < 0, accept the new solution, or else accept new solution along the possibility 𝑒−𝑑𝑓𝑇 . Stopping criteria are satisfied, present solution is optimum solution and result, next stop an algorithm, or else return to step 2 after minimizing temperature. The termination criteria is generally continuous count of new solutions which is not accepted or attained termination temperature.
Traditional SSA has problems like a slow convergence rate and less optimization accuracy. The SA-SSA implemented a logistic map for population initialization that enhanced population diversity. The strategy of symmetric adaptive population diversity is implemented to balancing development and exploration capacity of algorithm. At last, SA algorithm depended on symmetric perturbation to accept solution along some possibility.
3.3. Network Training on PAPR Reduction
The network is trained to efficiently minimize the PAPR while maintaining a better BER performance. Two main objectives such as PAPR reduction and BER minimization is taken for training. This stage uses the based VAE method to develop the PAPR reduction method, which is trained with label data generated by Selective Clipping and Filtering (SCF) to minimize PAPR and the Bit Error Rate (BER) minimization. Primarily, SA-SSA based VAE method is needed to reconstruct the transmitting signal from received signal to make sure that BER remains constant. Then, SA-SSA-based VAE generated a broadcasting signal that exhibited less PAPR. The encoding of SA-SSA based VAE method process training to determine respective constellation mapping from input data 𝑟𝑘 to outcome 𝑋𝑡 and decoding of SA-SSA based VAE method requires decoding of received signal. The mathematical formula for the respective loss function is given in Eq. (22),
Where, 𝑓(; 𝜃𝑓) and 𝑔(; 𝜃𝑔) represents parameters of encoding and decoding, 𝜀 represents noise in receiver end. Weight matrices, bias, and activation layer are represented by feasible matrix parameters of hidden variables that are 𝜃 = {𝑊, 𝑏}. After training, 𝜃𝑓 and 𝜃𝑔 that represents weights and bias of SA-SSA-based VAE defined through minimizing loss function and effective to random channel 𝐻 which is acquired by encoding and decoding. At the same time, the mathematical formula for the loss function 𝐿1(𝑟) to attain less PAPR is given in Eq. (23),
Here, the training procedure considers two stages. In the first stage of training, the accurate corruption stage, 𝜂 =𝐸[|𝜀|2]/𝐸[|𝑟|2] defined proportion of noise to signal power is identified through the loss function 𝐿1. In further stage of training procedure, weight and bias of SA-SSA based VAE (𝜃𝑓𝑎𝑛𝑑𝜃𝑔) are learnt by joint loss function 𝐿(𝑟, 𝑟̂), combining 𝐿1 and 𝐿2 which minimizes PAPR and BER. Mathematical formula to calculate 𝐿(𝑟, 𝑟̂) is given in Eq. (24),
Where 𝜆 is weight parameter which determines which loss is important. The lesser 𝜆 resulted in good BER performance and low PAPR minimization. Hence, better compromise among PAPR and BER is attained through varying values of 𝜆.
4. EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
In this section, the proposed SA-SSA based VAE is simulated with MATLAB R2021b version 9.11 with system requirements of i6 processor and 16GB RAM. The performance of the proposed SA-SSA based VAE is analyzed with BER, SER and CCDF. The results of proposed method are analyzed under various subcarriers such as 64, 128, 256, 512, and 1024. Table 1 describes simulation parameters.
Table 1. Simulation parameters.
4.1. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
In this section, the performance of developed SA-SSA based VAE method is analyzed with characteristics of BER, SER and PAPR under sub-carriers 64 and 128. The existing methods considered for evaluating the proposed method are Original OFDM, Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and SSA.
4.1.1. BER Analysis
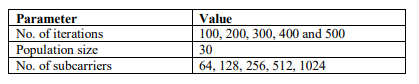
The BER is referred to as count of bit errors separated through the whole count of broadcasted bits during time intervals. Figure 3 shows performance of BER with 64 sub-carriers and Figure 4 shows performance of BER with 128 sub-carriers. Figures 3 and 4 show the proposed method has less BER than other existing methods for 64 and 128 sub-carriers.
Figure 3. BER vs SNR (Sub-carrier = 64)
Figure 4. BER vs SNR (Sub-carrier = 128)
4.1.2. SER Analysis
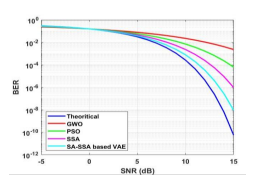
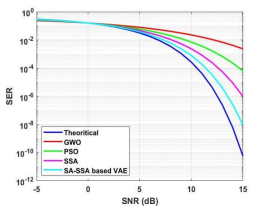
The SER is utilized for evaluating the performance of digital communication systems that quantify the possibility of incorrect decoding of broadcasting symbols in the presence of channel impairments. Figure 5 shows performance of SER with 64 sub-carriers and Figure 6 shows the performance of SER with 128 sub-carriers. Figures 5 and 6 show that the proposed method has less SER than other existing methods for 64 and 128 sub-carriers.
Figure 5. SER vs SNR (Sub-carrier = 64)
Figure 6. Iteration vs SER (Sub-carrier = 128)
4.1.3. CCDF Analysis
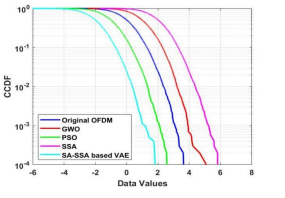
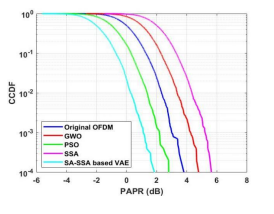
The CCDF attained considerable PAPR reduction without distortion. It generates complex data about signals in 5G networks and it gives PAPR information required. Figure 7 shows performance of CCDF with 64 sub-carriers and Figure 8 shows performance of CCDF with 128 sub-carriers. Figures 7 and 8 show that the proposed method has less CCDF than other existing methods for 64 and 128 sub-carriers.
Figure 7. CCDF vs PAPR (Sub-carrier = 64)
Figure 8. CCDF vs PAPR (Sub-carrier = 128)
4.2. Comparative Analysis
The proposed SA-SSA based VAE method is compared to existing techniques like HPT-SSAE [20], Hybrid–PTS [21], TDS-IM-OFDM-SS [22] and C-ANN [23] under various sub-carriers like 64, 128, 256, 512 and 1024. The comparisons are performed based on characteristics of BER, SER, and PAPR (dB) which are represented in Table 2. The proposed SA-SSA based VAE method attained less BER, SER and PAPR than other existing methods which are compared.
Table 2. Comparative Analysis.
4.3. Discussion
This section, compared the proposed SA-SSA-based VAE method with other existing techniques like HPT-SSAE [20], Hybrid–PTS [21], TDS-IM-OFDM-SS [22], and C-ANN [23] under various sub-carriers like 64, 128, 256, 512 and 1024. The comparison depends on the metrics of BER, SER, and PAPR which are shown in above Table 2. The HPT-SSAE [20] method applied the subcarriers of 128, 256, and 512 and showed more effective performance than other methods compared. However, it has higher BER, SER, and PAPR than the proposed method. The Hybrid– PTS [21] method has a high PAPR of 10.6 for 1024 subcarriers which is higher than other methods compared in Table 2. The TDS-IM-OFDM-SS [22] and C-ANN [23] methods applied a single subcarrier and obtained high PAPR of 9 dB and 5.5 dB. The proposed method applied five subcarriers and obtained less PAPR of 1.9 dB, 2.0 dB, 2.4 dB, 2.8 dB, and 3.2 dB for 64, 128, 256, 512 and 1024 subcarriers which are less than other existing methods compared in table 2.
5. CONCLUSION
This research proposed an SA-SSA based VAE for PAPR reduction which minimizes the peaks in the OFDM system. The SA-SSA-based VAE method is used to develop a peak-average canceling signal depending on input signal. The constellation mapping and remapping of symbols are considered in every subcarrier by utilizing VAE method that minimizes BER and PAPR in OFDM systems. To further improve performance of VAE, developed SA-SSA algorithm that tuned the hyperparameters of the VAE method. The performance of developed method is analyzed along with characteristics of BER, SER, and CCDF under various subcarriers. The proposed method obtained less PAPR of 1.9 dB, 2.0 dB, 2.4 dB, 2.8 dB and 3.2 dB for 64, 128, 256, 512 and 1024 subcarriers which is less than other existing methods. In future, different optimization algorithms will be utilized in PTS technique for PAPR reduction.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
[1] Farhadi, Hamed, Johan Haraldson, & Mårten Sundberg, (2023) “A deep learning receiver for nonlinear transmitter”, IEEE Access, Vol. 11, pp. 2796-2803.
[2] Amina Darghouthi, Abdelhakim Khlifi and Belgacem Chibani,(2024)” Real Time Parameter Estimation for Adaptive OFDM/OTFS Selection”, International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.16, No.4,pp. 109-129.
[3] Fatma Ben Salah, Abdelhakim Khlifi, Marwa Rjili, Amina Darghouthi and Belgacem Chibani,(2025)”EnhancedPapr Reduction In OFDM Systems Using Adaptive Clipping With Dynamic Thresholds”, International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.17, No.1,pp.45-58.
[4] Ravi Hosamani,Yerriswamy,(2023)”CHANNEL ESTIMATION IN MIMO OFDM SYSTEMS WITH TAPPED DELAY LINE MODEL”,International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.6, pp 97-113.
[5] Zhang, Tianhao, Zhengrong Tong, Weihua Zhang, Hao Wang, & Peng Li, (2022) “A novel PAPR reduction scheme based on joint traditional algorithm and machine learning for CO-OFDM systems”, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, Vol. 35, No. 8, pp. 418-421.
[6] Cherif, Maha, Ahlem Arfaoui, Rafik Zayani, & Ridha Bouallegue, (2023) “End-to-end deep learning for multipair two-way massive MIMO with PA impairments”, IEEE Systems Journal, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 3150-3159.
[7] Li, Zhijie, Ningde Jin, Xin Wang, &Jidong Wei, (2020) “Extreme learning machine-based tone reservation scheme for OFDM systems”, IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, Vol. 10, No. 1, pp. 30-33.
[8] Mangipudi, Pavan Kumar, Maneesh Merugu, Janise McNair, John Terry, & David Veney, (2023) “PESTnet-Pre-IFFT PAPR Estimation using Neural Networks for Improved OFDM Systems”, In: 2023 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), IEEE, Glasgow, United Kingdom, pp. 1-7.
[9] Kota, P.N., Gaikwad, A.N. ,”Fireflies algorithm based optimal scrambling to reduce PAPR in SFBC based MIMO-OFDM”, International Journal on Communications Antenna and Propagation,Vol.7, No.7, pp.626-634.
[10] Zhang, Xiaoyu, Thien Van Luong, Periklis Petropoulos, & Lajos Hanzo, (2021) “Machine-learningaided optical OFDM for intensity modulated direct detection”, Journal of Lightwave Technology, Vol. 40, No. 8, pp. 2357-2369
[11] Baruffa, Giuseppe, Luca Rugini, Fabrizio Frescura, & Paolo Banelli, (2023) “Low-complexity PAPR reduction by coded data insertion on DVB-T2 reserved carriers”, IEEE Access, Vol. 11, pp. 73377-73393.
[12] Nguyen, Quang, The Khai Nguyen, Ha H. Nguyen, & Brian Berscheid, (2022) “Novel PAPR reduction algorithms for OFDM signals”, IEEE Access, Vol. 10, pp. 77452-77461.
[13] Xue, Xingsi, SatheeshKumar Palanisamy, A. Manikandan, DhanaSekaran Selvaraj, Osamah Ibrahim Khalaf, & Ghaida Muttashar Abdulsahib, (2023) “A Novel partial sequence technique based Chaotic biogeography optimization for PAPR reduction in generalized frequency division multiplexing waveform”, Heliyon, Vol. 9, No. 9 p. e19451.
[14] Narottama, Bhaskara, Zina Mohamed, & Sonia Aïssa, (2023) “Quantum machine learning for nextG wireless communications: Fundamentals and the path ahead”, IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, Vol. 4, pp. 2204-2224.
[15] Aydin, Volkan, &GokceHacioglu, (2024) “Enhanced PAPR reduction in DCO-OFDM using multipoint constellations and DPSO optimization”, Neural Computing and Applications, Vol. 36, No. 11, pp. 5747-5756.
[16] Tu, Yung-Ping, Zi-Teng Zhan, & Yung-Fa Huang, (2024) “A Novel Alternating μ-Law Companding Algorithm for PAPR Reduction in OFDM Systems”, Electronics, Vol. 13, No. 4, p. 694.
[17] Tuli, Esmot Ara, Rubina Akter, Jae Min Lee, & Dong‐Seong Kim, (2024) “Whale optimization‐based PTS scheme for PAPR reduction in UFMC systems”, IET Communications, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp. 187-195.
[18] Zhu, Hequn, Xu Zhao, Dejian Li, Yubo Wang, Yubing Zhang, Zhenghao Li, & Han Liu, (2024) “A reduced peak-to-average power ratio algorithm based on PMI mode in NR”, Telecommunication Systems, Vol. 85, No. 4, pp. 539-550.
[19] Kim, Hyungcheol, &Sangwook Nam, (2024) “Asymmetric Decomposition of Single Carrier QAM for Efficiency Enhancement of Pas”, IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 72, No. 8, pp. 4986-4997.
[20] Jayamathi, A, & Jayasankar, T. (2022) “Deep learning based stacked sparse autoencoder for PAPR reduction in OFDM systems”, Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, Vol. 31, No. 1, pp. 311- 324.
[21] Ramavath, Srinivas, Umesh Chandra Samal, Bhargav Appasani, & Mohammad S. Khan, (2024) “A
hybrid approach based on companding and PTS methods for PAPR reduction of 5G waveforms”, International Journal of Electronics Letters, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 330-342.
[22] Esmaiel, Hamada, Hussein A. Leftah, Naveed Ur Rehman Junejo, &Haixin Sun, (2023) “Deep Learning-Based Index Modulation for Underground Communications”, IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, Vol. 4, pp. 2122 – 2132.
[23] Eldukhri, Eldaw E., & Mohammed I. Al‐Rayif, (2024) “A conditionally applied neural network algorithm for PAPR reduction without the use of a recovery process”, ETRI Journal, Vol. 46, No. 2, pp. 227-237.
[24] Abdullah, Ezmin, KaharudinDimyati, Wan Norsyafizan W. Muhamad, Nurain Izzati Shuhaimi, Roslina Mohamad, & Nabil M. Hidayat (2024) “Deep learning based asymmetrical autoencoder for PAPR reduction of CP-OFDM systems”, Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, Vol. 50, p. 101608.
[25] Valluri, Sivaprasad, Chakravarthy Gunturu, Sowbhagya Appalla, Anupam Kajale, & V. V. Mani, (2023) “Testbed for a Novel Approach to Minimizing the PAPR of 5G Systems”, IEEE Access, Vol. 11, pp. 36753-36762.
[26] Singh, Abhiranjan& Seemanti Saha, (2022) “Machine/deep learning based estimation and detection in OFDM communication systems with various channel imperfections”, Wireless Networks, Vol. 28, No. 6, pp. 2637-2650.
AUTHORS
Prabhakar Kota, holds a Ph.D. degree in Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering from SPPU University, Pune, awarded in 2018. and a Master of Technology (MTech) from COEP, Pune, completed in 2008. He is now a Associate Professor at MES Wadia college of engineering, Pune, India. His research interests include signal processing, and wireless Communication systems, Internet of things
Pravin B Chopade, is currently working as an Associate Professor of E&Tc in M. E. S. College of Engineering, Pune-01 .He holds BE in Electronics , ME in Electronics and PhD in Electronics and Telecommunications Engineering and has more than 20 plus publication in reputed national and international journals. He has published patent based on suerresolution of images using hardware platform. His research papers have been widely cited, in technical papers and reference books He is member of IETE and ISTE. His area of interest is image processing and signal processing.
Bhagavat D. Jadhav, received the B.E. degree in Electronics engineering from Pune University, Pune India, in 2002, M.Tech. and Ph.D. degrees from Savitribai Phule Pune University, India, in 2008 and 2017 respectively in Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering. Since July 2005, he has been with the Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering and currently he is working as Professor and Dean Controller of Examinations. His current research interests include Signal and Image processing. He is a Life Member of the Indian Society for Technical Education (ISTE). He has filed two patents and published more than twenty papers in various IEEE, Elsevier, Springer conferences and reputed journals.
Dr. Shriram Sadashiv Kulkarni, is working as Associate Professor and Head of Information Technology Department of Sinhgad Academy of Engineering, Pune, India. He has done. his Ph.D. in Electronics and Telecommunication from Sinhgad College of Engineering, affiliated with Savitribai Phule Pune University in 2021. He received M. E. in Electronics and Telecommunication from Government College of Engineering, Pune in 2004. His areas of research are Wireless Communication, Signal and Image Processing
Prof. Dr. Pravin Marotrao Ghate, is a graduate in Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering with a post-graduate degree in Electronics Engineering . For doctorate, He did research in the area of Speech Processing with design and development of Speech synthesis Methods for improving the quality of syllable for Marathi Language Prof. Dr.Pravin Ghate is the Professor in JSPM’s Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering, Tathwade, Pune and Professor at Department of E&Tc Engineering. He has 17 technical published papers in National & International Journals and Conferences. His research papers have been widely cited, in technical papers and reference books. He is guiding 2 Doctoral students and 15 postgraduate students and is credited with the establishment of a Project laboratory (Electronics ). He had worked on two major projects sponsored by Matrix Automation and SPPU. His research has led to 02 patents being registered to his credit. He is actively associated with various prestigious Education/Research organisations like Dr Babasaheb Marathwada Ambedkar University Aurangabd as External examiner and Matrix Automation in Pune for R&D activities & member of Purchase Committee. He is also a Member of Indian Society of Technical Education & Society of Automotive Engineers.